What is sleep apnea?
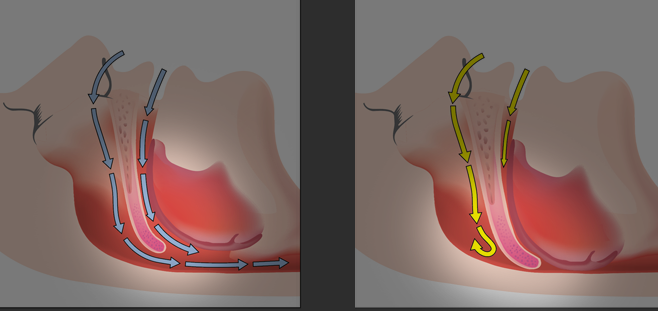
Sleep apnea is a serious but common and treatable disorder that causes a person to stop breathing during sleep. In severe cases, breathing stops several hundred times per night.
An “apnea” occurs when the back of the airway collapses or becomes blocked. That may cause the person to snore, then gasp for air as they wake briefly to unblock the airway.
Without treatment, sleep apnea increases the risk of major health problems, including heart attack, stroke, diabetes, and depression. Untreated sleep apnea also increases the likelihood of safety incidents or accidents caused by falling asleep during activities.
Why is this a public health issue?
Obstructive sleep apnea, the most common type of sleep apnea, affects almost 30 million Americans, or 12% of the U.S. adult population. However, 80% of these cases are still undiagnosed, meaning almost 10 million people experience the effects of undiagnosed sleep apnea, leading to increased health care costs, more workplace accidents and vehicle crashes, and lost productivity.
Learn more about obstructive sleep apnea and its impact on public health in the OSA National Indicator Report.
